A Guide to Fiber Optic Color Codes
Fiber optic cables are thin, flexible strands of glass or plastic used in telecommunications, data transmission and other applications where high-speed, high-bandwidth data transfer is required.
In complex network infrastructures, engineers and technicians rely on color coding as an integral part of cable identification. Color codes provide quick visual identification, making it easier to track and manage multiple cables at a time. Use this guide to understand the basics of color coding and why it's important to adhere to certain standards.
Overview of Fiber Color Code Standards

Fiber optic cables are color-coded to identify their type, core size and cladding material. Adhering to standardized color codes ensures compliance with industry regulations and best practices, making it easier to track and manage multiple cables in a complex network infrastructure. A standardized color-coding scheme also enables seamless integration and compatibility across different manufacturers and cable types.
There are several different fiber color code standards for fiber optic cables, so it’s important to choose the one that is most appropriate for your application. The most common standards are TIA-598C, ANSI/TIA-568.3-D, ISO/IEC 11801 and ITU-T G.652.
- TIA-598C: TIA-598C is an American National Standard for color-coding optical fiber cables and the most recognized system worldwide, developed by the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA). This standard defines colors for both single-mode and multimode fibers to facilitate identification and management of the fibers during installation, termination and maintenance processes.
- ANSI/TIA-568.3-D: ANSI/TIA-568.3-D defines the physical layer requirements for twisted pair cabling and connectors in commercial building telecommunications cabling systems. It’s an important standard for anyone who designs, installs or maintains commercial building telecommunications cabling systems, ensuring these systems are installed and tested properly.
- ISO/IEC 11801: ISO/IEC 11801 is an international standard that defines a color-coding system for particularly complex fiber optic cabling infrastructures. This standard specifies the colors that should be used for the outer jacket of the cable, as well as the colors of the individual fibers within the cable.
- ITU-T G.652: ITU-T G.652 is an international standard that describes the mechanical, geometrical and transmission characteristics of single-mode optical fiber and cables. It was developed by the Standardization Sector of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU-T).
Understanding Color Codes
Outer jacket colors
The outer jacket of a fiber optic cable is color coded to indicate the cable type.
- Yellow: OS1/OS2 single-mode fibers (SMF)
- Orange: OM1/OM2 multimode fibers (MMF)
- Aqua: OM3/OM4 multimode fibers
Inner fiber strand colors
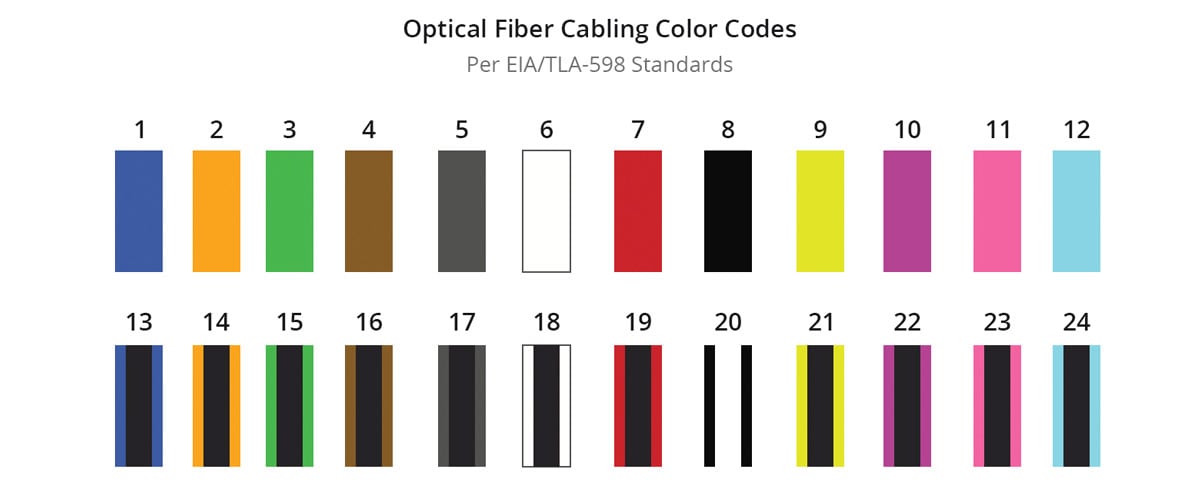
Within a multi-fiber cable, individual fibers adhere to a specific fiber optic cable color code. Each fiber is typically distinguished by color-coded jackets, buffers or tubes. As outlined in TIA-598, inner fibers are grouped into sets of 12 and numbered in a clockwise direction.
When a cable has more than 12 fiber strands (like a 24-fiber cable), the color code repeats. However, each 12-strand group should be identified in a unique way. For example, in a 24-strand cable, a stripe could be added to the second group to distinguish the new group from the previous one. The standard 12-color sequence is as follows:
| Fiber Number | Color | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Blue | |
| 2 | Orange | |
| 3 | Green | |
| 4 | Brown | |
| 5 | Grey | |
| 6 | White | |
| 7 | Red | |
| 8 | Black | |
| 9 | Yellow | |
| 10 | Violet | |
| 11 | Rose | |
| 12 | Aqua | |
Connector colors
Color codes are also used to identify the type of connector used on a fiber optic patch cord.
- Beige or black: Standard multimode OM1/OM2 fiber patch cords
- Aqua: OM3 cords
- Magenta: OM4 cords
- Blue: Single-mode UPC connections
- Green: Single-mode APC terminations
Note that it's essential to distinguish between UPC and APC connectors as they cannot be mixed.
International Variations in Color Coding Standards
While the TIA-598C standard is widely accepted and used in North America, other countries and regions may have their own color-coding standards for fiber optic cables. Some of the most common international variations include:
- Europe: In Europe, the CENELEC EN 50173 standard is often used for color-coding fiber optic cables. This standard is similar to TIA-598C, but there are some minor differences in the colors used for certain types of cables.
- Asia: In Asia, the IEC 60304 standard is commonly used for color-coding fiber optic cables. This standard is similar to TIA-598C and CENELEC EN 50173, but there are some differences in the colors used for certain types of cables and connectors.
- South America: In South America, the ABNT NBR 14703 standard is often used for color-coding fiber optic cables. This standard is similar to TIA-598C, but there are some differences in the colors used for certain types of cables and connectors.
When working in a global environment, it’s important to be aware of different international standards to ensure that cables are properly identified, and that there’s no confusion or miscommunication. See how Brady can help reduce confusion with our wire and cable labels.
Practical Applications of Color Codes in Real-World Settings
Fiber optic color coding is used in a variety of applications to identify and manage different types of fiber optic cables and connectors.
- Data centers: Fiber optic cables are used extensively in data centers to connect servers, storage devices and other networking equipment. Color coding makes it easy to trace cables from one end to the other. Our wrap around cable labels work particularly well as fiber optic labels and will create additional clarity.
- Telecommunications networks: Fiber optic cables are also used in telecommunications networks to carry voice, data and video traffic. Color coding is used to identify cables and troubleshoot problems.
- Industrial settings: In industrial settings, color coding is important to properly install and maintain fiber optic cables, which are used to connect sensors, actuators and other devices.
- Medical applications: In medical settings, fiber optic cables play a crucial role in various procedures such as endoscopy and laser surgery. To ensure safety and effectiveness during these procedures, a color-coding system is utilized to differentiate between different cables, allowing medical professionals to quickly identify and select the appropriate cable for their specific needs.

